2018年第四季度课题组发表SCI论文12篇,其中2区及以上SCI论文4篇。
微纳器件及系统方面:
1. Qiao Xu, Bo Dai,* Ziao Jiao, Ruijin Hong, Zhuoqin Yang, Dawei Zhang, and Songlin Zhuang, Fabrication of large micro-structured high-numerical-aperture optofluidic compound eyes with tunable angle of view, Optics Express, 2018, 26(25): 33356-33365.【2018年12月】2区
2. Kang Yi, Zhang Leihong*, Zhang Dawei, Optical encryption based on ghost imaging and public key cryptography, Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2018, 111: 58-64.【2018年12月】2区
微纳光电材料方面:
1. Changda Gao, Hui Lin*, Dawei Zhang, Ruijin Hong, Chunxian Tao, Zhaoxia Han, Eu2+-activated blue-emitting glass phosphor derived from Eu3+ exchanged USY zeolites by thermal treatment in reducing atmosphere, Ceramics International, 2018, 44: 19547-19553. 【2018年11月】2区
2. Jiqing Lian, Dawei Zhang*, Ruijin Hong, Peizhen Qiu, Taiguo Lv and Daohua Zhang, Defect-Induced Tunable Permittivity of Epsilon-Near-Zero in Indium Tin Oxide Thin Films, Nanomaterials, 2018, 8: 922.【2018年11月】2区
论文创新工作概要介绍
一、微纳器件及系统方面:
1. Qiao Xu, Bo Dai,* Ziao Jiao, Ruijin Hong, Zhuoqin Yang, Dawei Zhang, and Songlin Zhuang, Fabrication of large micro-structured high-numerical-aperture optofluidic compound eyes with tunable angle of view, Optics Express, 2018, 26(25): 33356-33365.【2018年12月】2区
Abstract:
A large optofluidic compound eye is developed by using a straightforward, rapid and low-cost technique. The angle of view of the compound eye can be adjusted by injecting deionized water/calcium chloride solution of different volume into the optofluidic chip. Optofluidic compound eyes containing about 78,000 microlenses of 50 μm diameter are fabricated for analysis. The angle of view can be tuned up to 104º. With the deformation of the compound eye, the focal length of the microlenses increases due to the variation in profile. Owing to the non-uniform strain over the compound eye, the central lenses experience more variation. Furthermore, optical imaging of the compound eye is demonstrated and sharp images can be obtained from the omnidirectional microlenses.
摘要:
本文介绍了一种简单、快速以及低成本的方式制备一种大尺寸的光流控复眼。可以通过调节注入的氯化钙匹配液体积来调节该复眼的视角。该光流控复眼结构包含了78000个50 μm直径的微透镜,视角调节可达到104°。伴随着复眼的形变,小透镜的焦距随着表面形变而增加。由于复眼结构上承受的不均匀拉力,中间区域的透镜会发生更大的形变。此外,本文也展示了该复眼结构的光学成像效果,并且从全方位的微透镜中获得了清晰的图像。
关键数据:
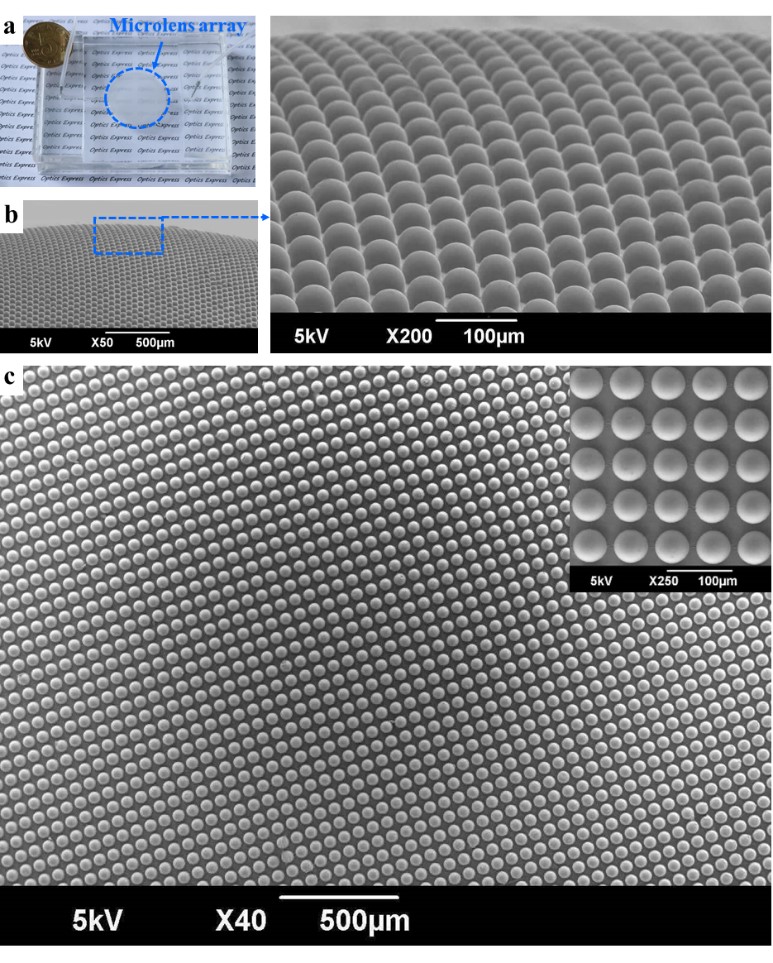
(a) Microfluidic Compound Eye Structural Chip Diagram, (b) and (c) Side-looking and overlooking enlarged SEM images of Compound Eye Structures.
(a) 微流控复眼结构芯片图,(b) 和 (c) 复眼结构的侧视及俯视面放大后的SEM图像。
2. Kang Yi, Zhang Leihong*, Zhang Dawei, Optical encryption based on ghost imaging and public key cryptography, Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2018, 111: 58-64.【2018年12月】2区
Abstract:
In this paper, according to the phase object in the ghost imaging has a stealth effect, we proposed an optical encryption method based on compressive ghost imaging and public key cryptography. This method solves the key distribution problem of ghost imaging encryption, and reduces the additional cost of establishing security channels. The simulation results verify the feasibility, security and robustness of the proposed encryption scheme. This technique can be immediately applied to encryption and data storage with the advantages of high-safety, high-robustness and low-cost.
摘要:
本文根据鬼像中的相位对象具有隐形效应,提出了一种基于压缩鬼像和公钥密码的光学加密方法。该方法解决了鬼像加密的密钥分配问题,降低了建立安全通道的额外成本。仿真结果验证了所提出的加密方案的可行性、安全性和鲁棒性。该技术具有安全性高、鲁棒性强、成本低等优点,可直接应用于光学加密和数据存储。
关键数据:
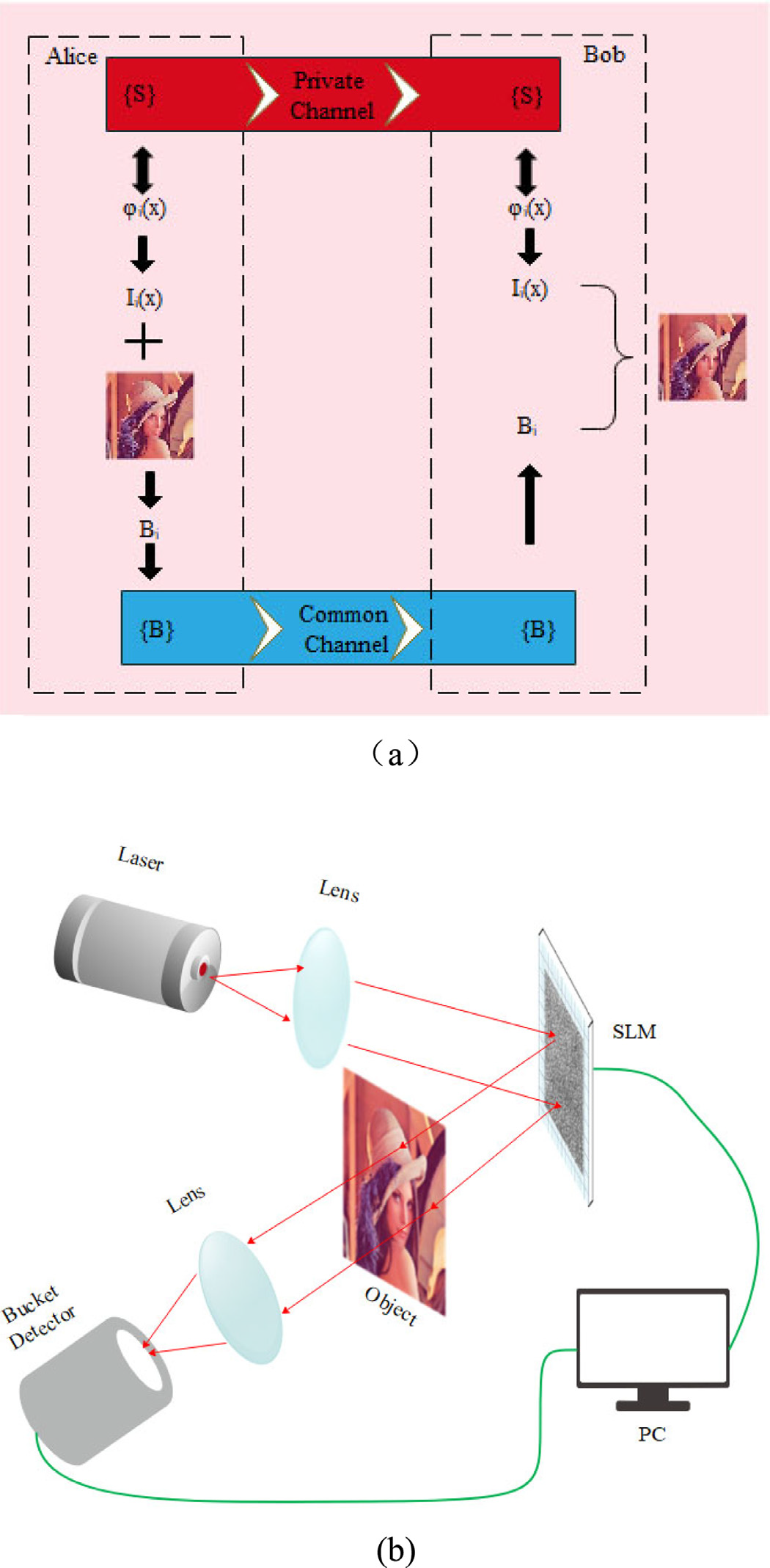
Scheme of the encryption method based on GI. (a) Block diagram showing encryption/decryption procedure. (b) Experimental setup for GI.
基于GI的加密方法方案。(a)显示加密/解密过程的框图。(b)GI的实验装置。
二、微纳光电材料方面:
1. Changda Gao, Hui Lin*, Dawei Zhang, Ruijin Hong, Chunxian Tao, Zhaoxia Han, Eu2+-activated blue-emitting glass phosphor derived from Eu3+ exchanged USY zeolites by thermal treatment in reducing atmosphere, Ceramics International, 2018, 44: 19547-19553. 【2018年11月】2区
Abstract:
In this work, we report a facile method to prepare Eu2+ activated blue-emitting glass phosphor via loading Eu3+into USY (Na28Si168Al28O384·240H2O, Si/Al ratio=6) zeolites’ cavities followed by thermal treatment in reducing atmosphere. The zeolites powders containing Eu3+ were treated at different temperatures from 800 °C to1200 °C in flowing 5%H2 +95%N2 ambient. The photoluminescence properties were investigated on aspects of the emission and excitation spectra, internal quantum efficiency (IQE), thermal stability and the fluorescence lifetime. The XRD patterns showed that the sample calcined at 950 °C was of pure glassy state. Under the broad 200-430 nm excitation, a strong blue emission band peaked at 451 nm with a full width of half maximum (FWHM) value of 74 nm was observed for this sample. Under the 365 nm excitation, the samples treated at different temperatures showed monotone red shift in the emission peak wavelengths with the thermal treatment temperature increasing. Transparent glass sheets were obtained from the glass phosphor powders by spark plasma sintering (SPS) at 1200 °C, 1250 °C and 1300 °C. The optical transmittance and thermal conductivity of transparent glass sheets were measured. The results indicated that this glass phosphor may be a potential candidate material for white LEDs.
摘要:
本文工作报道了将Eu3+离子通过离子交换引入USY型沸石(Na28Si168Al28O384·240H2O, Si/Al比=6)孔道内,后在还原性气氛中热处理获得Eu2+离子激活蓝色发光玻璃态荧光材料的便捷方法。在5%H2+95%N2流动气氛下,在800℃至1200℃范围内不同温度下含有Eu3+离子的沸石粉末。从发射和激发光谱、内量子效率(IQE)、荧光热猝灭和荧光寿命这些方面研究了样品的光致发光性能。XRD图谱显示在950℃下煅烧的样品是纯玻璃态的。在200-430 nm宽带激发下,观察到该样品峰值波长在451 nm的蓝光发射,发射峰半峰全宽(FWHM)值为74 nm。在365 nm激发下,在不同温度下处理获得的样品的发射峰值波长随热处理温度升高呈现单调红移。通过放电等离子体烧结(SPS)在1200℃,1250℃和1300℃下烧结玻璃荧光体粉末获得透明玻璃板。测量了透明玻璃板的光学透射率和热导率。结果表明,该玻璃态荧光材料可用做白光LED的潜在候选材料。
关键数据:
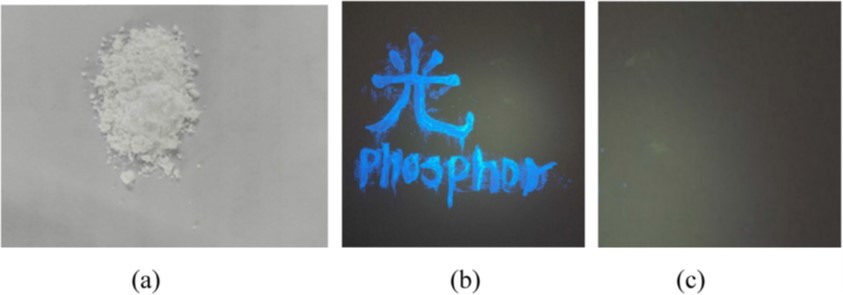
The blue-emitting phosphor synthesized at 950 °C (b) The words on the wall with (b) and without (c) a 365 nm ultraviolet flashlight illumination.
在950 °C下还原性流动气氛中热处理获得的蓝光发光荧光粉末照片(a);将该粉末样品涂敷在墙壁上,用365 nm紫外光手电筒照射样品的发光照片(b);图(c)是没有紫外光手电筒照射样品时的照片。
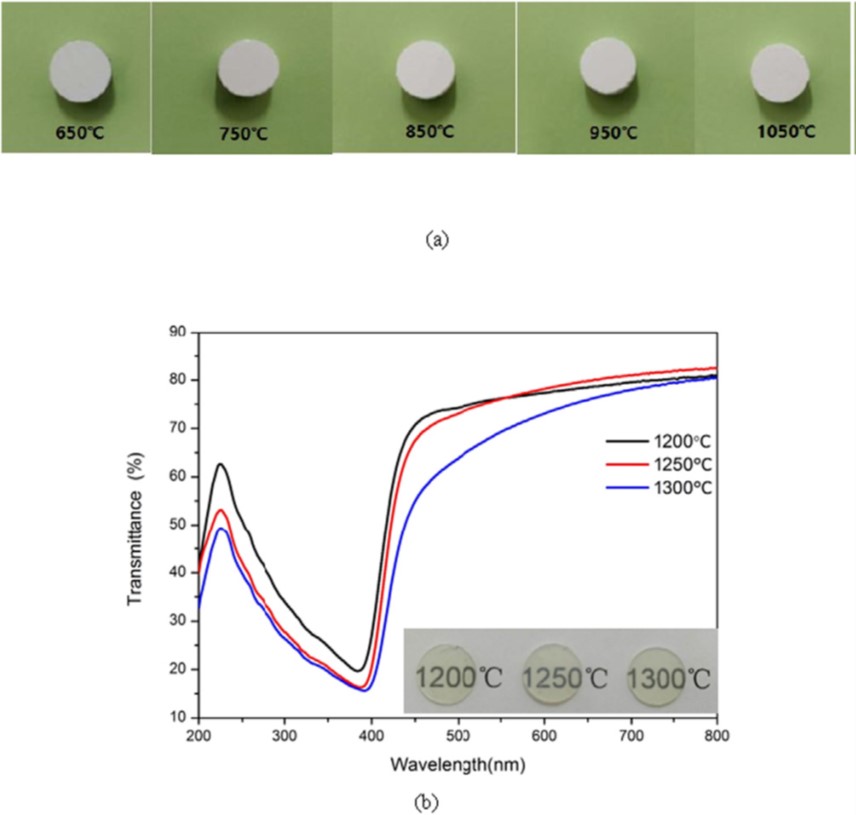
图(a) Photographs of the blue-emitting glass phosphor SPSed from 650 °C to 1050 °C with 50 MPa for 3 min (b) The optical transmittance of the as-prepared transparent glass sheets by SPS at 1200 °C, 1250 °C and 1300 °C for 3min. The inset image shows the corresponding photographs of the as-prepared transparent glass sheets.
图(a)采用SPS在650 °C至1050 °C 范围,50 MPa 下保温3 min所获得蓝色发光荧光材料的照片;图(b)是采用SPS在1200 °C, 1250 °C和1300 °C温度下保温3 min获得透明玻璃样品的光学透过率曲线,图(b)中插图是样品的照片。
2. Jiqing Lian, Dawei Zhang*, Ruijin Hong, Peizhen Qiu, Taiguo Lv and Daohua Zhang, Defect-Induced Tunable Permittivity of Epsilon-Near-Zero in Indium Tin Oxide Thin Films, Nanomaterials, 2018, 8: 922.【2018年11月】2区
Abstract:
Defect-induced tunable permittivity of Epsilon-Near-Zero (ENZ) in indium tin oxide (ITO) thin films via annealing at different temperatures with mixed gases (98% Ar, 2% O2) was reported. Red-shift of λENZ (Epsilon-Near-Zero wavelength) from 1422 nm to 1995 nm in wavelength was observed. The modulation of permittivity is dominated by the transformation of plasma oscillation frequency and carrier concentration depending on Drude model, which was produced by the formation of structural defects and the reduction of oxygen vacancy defects during annealing. The evolution of defects can be inferred by means of X-ray diffraction (XRD), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and Raman spectroscopy. The optical bandgaps (Eg) were investigated to explain the existence of defect states. And the formation of structure defects and the electric field enhancement were further verified by finite-difference time domain (FDTD) simulation.
摘要:
本文报道了缺陷诱导的不同温度、混合气体(98%Ar,2%O2)环境下退火处理的铟锡氧化物(ITO)薄膜的近零介电常数(ENZ)的可调特性。实现了ITO薄膜ENZ波长在1422~1995 nm波长范围的调控。由Drude模型可知,介电常数主要由等离子体振荡频率和载流子浓度决定的,而两者的变化是由退火过程中结构缺陷的形成和氧空位缺陷的减少产生所共同导致的。我们利用X射线衍射仪、原子力显微镜、和拉曼光谱仪表征并分析了薄膜中缺陷的演变。同时对ITO薄膜的光学带隙进行了研究,以解释缺陷态能级的存在。最后通过时域有限差分法(FDTD)模拟、验证了结构缺陷的形成和薄膜表面电场的增强。
关键数据:
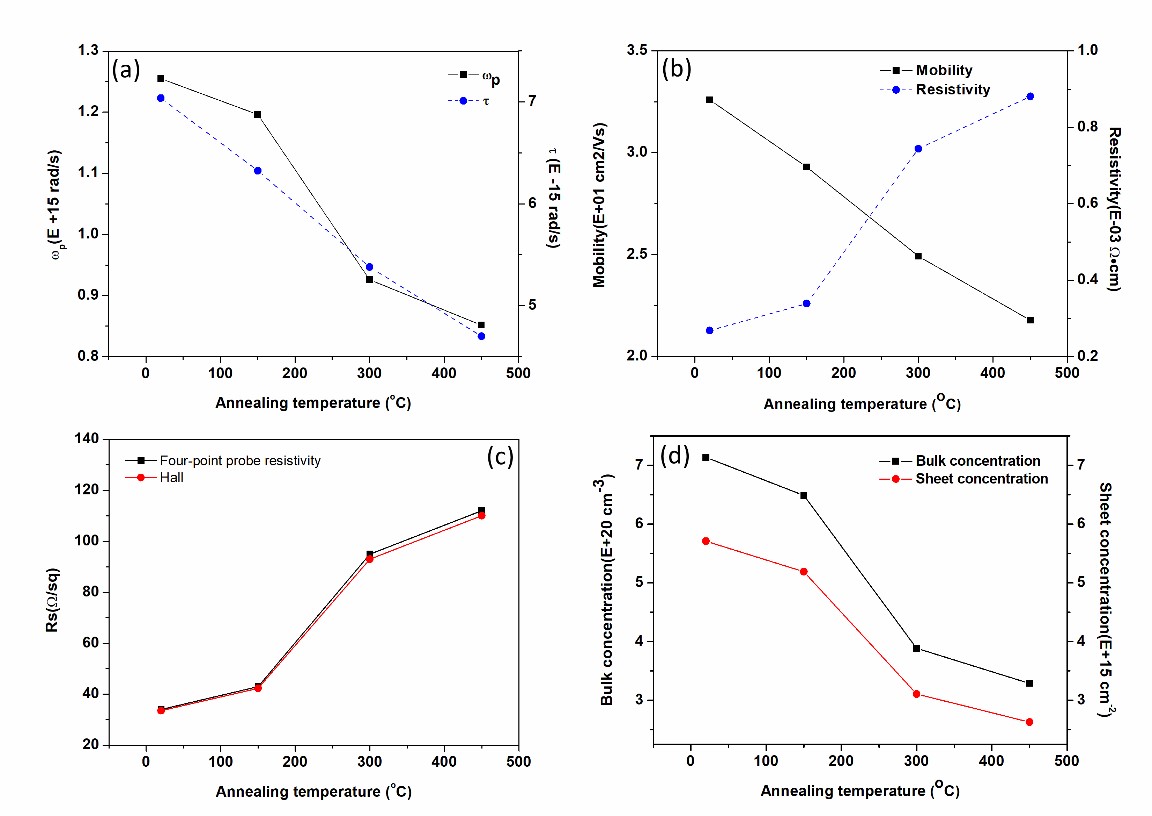
(a) The calculatedplasma frequency ωp and carrier relaxation time τ as a function of annealing temperature. (b) The resistivity ρ and electron mobility μ obtained from Hall Effect measurement. (c) The compared values of sheet resistance Rs measured by Hall Effect measurements and four-point probe resistivity measurement system. (d) The measured bulk carrier concentration n and sheet carrier concentration n'.
ITO薄膜的等离子特性和电学性质的表征与计算。
张大伟教授课题组