一、亮点工作
1.D. Zhang, Q. Xu, C. Fang, K. Wang, X.Wang, S. Zhuang, and B. Dai, “Fabrication of microlens array by thermallyharnessing surface tension of photosensitive gel film beneath microholes,” ACS Applied Material and Interfaces, vol. 9, no. 19, pp. 16604–16609, Apr.2017.(IF=7.145)
基于温度操控光敏胶表面张力的方法制作微透镜阵列
摘要:本文描述了一种快速制备低成本、高孔径值光敏胶微透镜阵列的方法,该微透镜阵列具有灵活的曲率可控性。在硅孔阵列模具下放置一层紫外固化胶膜,通过热处理来调控光敏胶的表面张力和空气与光敏胶界面间不同的压力,然后通过紫外光将凹的界面固化形成凹的微透镜阵列。这种光固化微透镜阵列有高硬度和高熔点的特点,并且能作为模具,复制出相同比例的微凸透镜。该方法制备的微透镜阵列具有均匀一致的形状和光滑的表面,在成像和聚焦性能方面,这种微凹透镜阵列和微凸透镜阵列能够看到清晰一致的像和聚焦光斑。
Abstract:A rapid method is developed forfabricating low-cost and high-numerical-aperture photosensitive-gel microlensarrays (MLAs) with well-controlled curvatures. An UV-curable photosensitive gelfilm beneath the microholes of a silicon mold can be flexibly deformed by thermallymanipulating the surface tension of the photosensitive gel and the pressuredifference across the air-photosensitive-gel interface. The concave interfaceis then solidified through UV curing, forming an MLA with a concave curvature.The photocuredMLA has high mechanical and thermal strength and is suitable as amaster mold for the further production of convex MLAs. The fabricatedmicrolenses have uniform shapes and smooth surfaces. In a demonstration ofimaging and focusing performance, clear and uniform images and focused lightspots were observed using concave and convex MLAs.
关键数据
本文提出了一种简便、低成本制作微透镜阵列的方法,该方法通过控制微孔中光敏胶与空气界面的表面压强差,改变光敏胶表面张力,形成曲率可控的微透镜阵列。工作中通过精确控制制作工艺的参数,例如:旋涂光敏胶的厚度、微孔中的温度等,深入研究了光敏胶与空气界面曲率变化的物理机制。通过该方法,能够实现大曲面的微透镜阵列,数值孔径可达0.49,微透镜阵列的焦距调节范围从51.4微米到71.9微米。
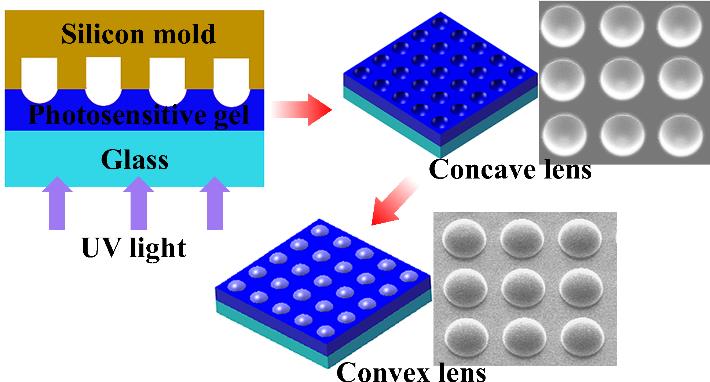
制作工艺示意图
Schematicof fabrication process
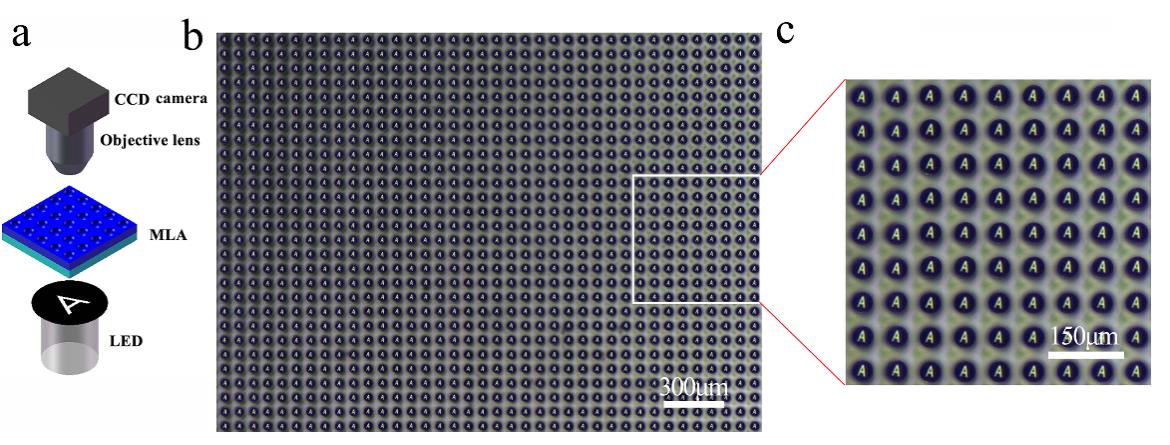
微透镜阵列成像性能测试
Test ofthe imaging performance of the fabricated concave MLA
该研究所提出的透镜阵列简单高效、成本低廉,在技术和方法上突破以往的限制。且获得的微透镜阵列子透镜表面均匀一致,成像清晰,焦距可调范围大,再结合其高强度、高熔点的特性。该技术能够支持猪病高通量检测技术及设备进一步的研究,包括高通量细胞的快速成像,样品的分析。另一方面该工作可以支持微流控芯片在细胞分选的研究。同时有望应用到微光学系统中,同时也为今后制备各种微光学元件开创了一条新的思路。
Asimple and low-cost method has been proposed and demonstrated to produce MLAsby harnessing the surface tension of the photosensitive gel and the pressuredifference across the air-photosensitive gel interface beneath the microholesof the silicon mold. By controlling the softbake temperature before molding,the curvature of the microlenses can be flexibly manipulated based on thetheory of capillarity and the Eotvos Ramsay–Shield relation so that the focallength variation from 51.4 μm to 71.9 μm can be achieved. Furthermore, themethod can effectively produce an MLA with a high aspect ratio and high NA (0.49)because of the significant deformation of the air–liquid interface.
Sincethe photocured-photosensitive-gel concave MLA has high mechanical and thermalstrength, the produced concave MLA can be used as a master mold to furtherduplicate convex MLAs. In the proposed method, no complex apparatus orexpensive material is required, and there is no time-consuming fabricationprocess. Thus, the method could be a new efficient approach to developingvarious micro-optical components.
2.Li. Zhenqing,Huang. Jiaxin, Yang. Bo, You. Qingxiang, Sekine. Shinichi, Zhang. Dawei,Yamaguchi. Yoshinori, “MiniaturizedGel Electrophoresis System for Fast Separation of Nucleic Acids ”, Sensors & Actuators B Chemical, Vol 254, pp 153-158, Jan.2017. (IF=5.401)
适用于核酸快速分离的微型化凝胶电泳仪
摘要:凝胶电泳是一种用于分离DNA, RNA及蛋白质常见方法。然而传统的凝胶电泳方法操作步骤繁琐,速度慢,涉及设备多,且需要专业的人员操作。本文报道了一中基于电泳芯片的凝胶电泳系统。通过在该设备上对50 bp DNA ladder分离,16个DNA片段可以在14分钟内快速分离与检测。同时,我们对口腔内的三种牙周病原菌(牙龈卟啉单胞菌(P.g), 福赛斯坦纳菌(T.f), 齿垢密螺旋体(T.d))的细菌实现了快速检测。数据表明,三种细菌可以在12分钟内被快速识别,且该设备对DNA的检测极限可达6.4 ng/μl。研究表明,该设备成本低,操作简单,可以极大提高DNA的检测效率,特别是对于第三世界国家生化研究人员核酸检测技术的提高具有重要意义。
Abstract: Slabgel electrophoresis (SGE) is very common tool for DNA, RNA and proteinanalysis, but it is tedious, labor-intensive, skill-dependent, and relativelyslow. Herein, we developed a biochip based SGE system, which can resolve theDNA fragments and record their separation process. By electrophoresis of 50 bpDNA ladder, we found that the 16 DNA fragments were effectively resolved within14 min. In order to validate its feasibility and practicability, we takeperiodontal pathogens (e.g., Porphyromonasgingivalis(P.g), Tannerela forsythia (T.f),and Treponemadenticola (T.d)) as an example by separating theirpolymerase chain reaction products. Experiments demonstrated that P.g, T.dand T.fwere diagnosed within 12 min,and the electrophoresis of P.g showedthat the detection limit of this system was about 6.4 ng/μl. Such a low costsystem is easy to operate, and can effectively improve SGE in the biologicalexperiment, especially for the labs in the third world countries.
关键数据
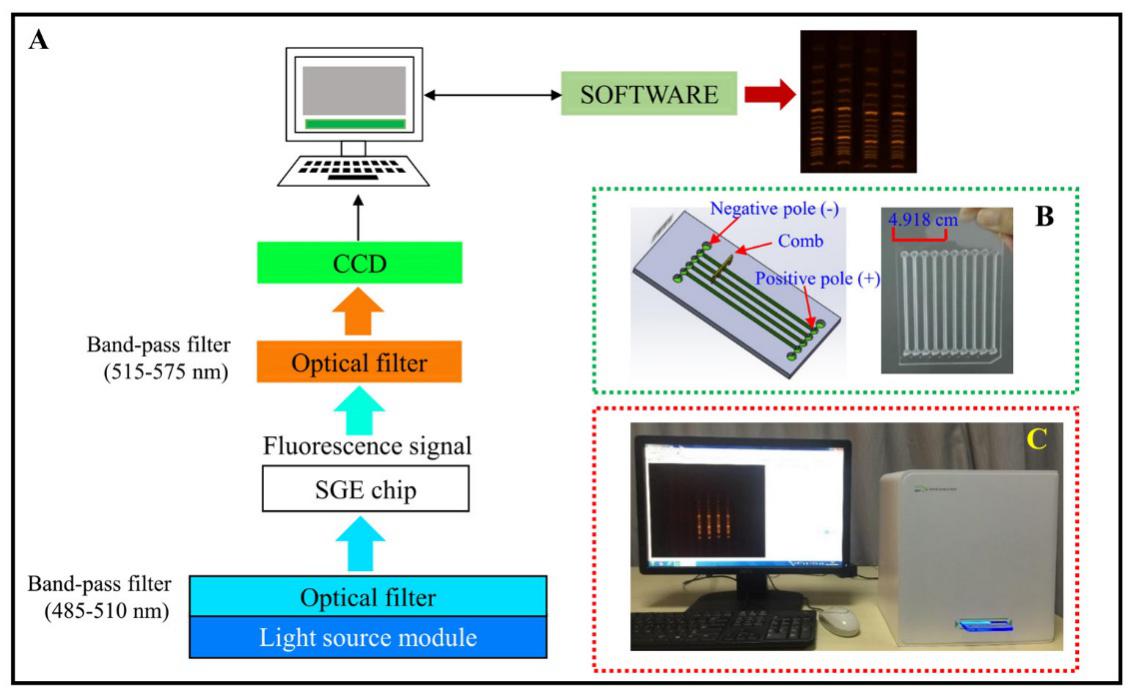
图1. 微型化电泳设备: (A)原理图 (B)电泳芯片 (C)实物图
Fig.1The miniaturized SGE system: (A) Schematic diagram. (B) The real SGE instrument.(C) The SGE chip.
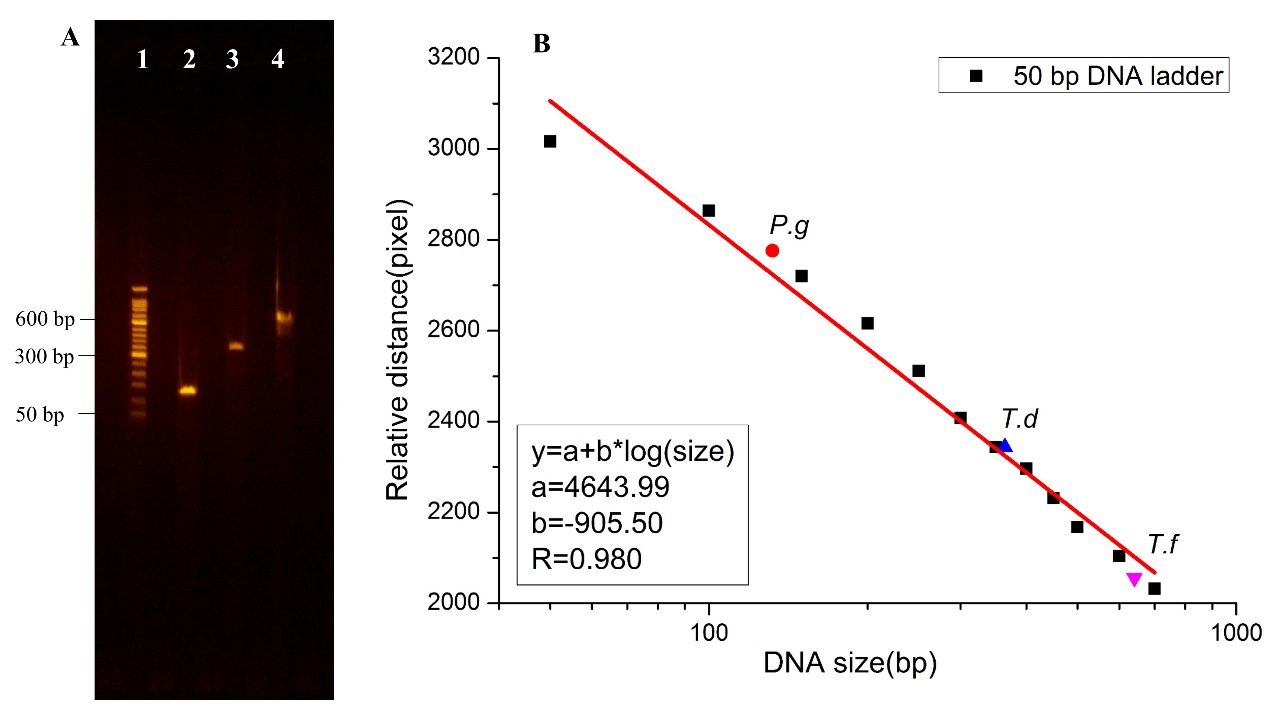
图2.(A)50 bp DNA ladder与牙周病原菌分离效果 (B)DNA迁移距离与DNA分子大小关系
Fig.2 (A) Separation of 50 bp DNAladder (lane 1) and PCR products of P.g(lane2), T.d(lane 3), and T.f (lane 4) in the self-developed SGEsystem. (B)The dependence of DNA migration distance on the molecular size.
3. Ming Jing, Ruijin Hong, Wen Shao, Hui Lin,Dawei Zhang, Songlin Zhuang and DaohuaZhang, Laser Induced PhotocatalyticActivity Enhancement of TiO2 Thin Films, 25(24), OpticsExpress, 2017 (A1132-A1138).(IF=3.344)
激光诱导下二氧化钛薄膜的光解水性能增强
摘要:本文中,通过激光辐照的方式实现了二氧化钛薄膜的光解水性能提高。比起未处理过的二氧化钛薄膜,激光处理后的薄膜的氢气产量比原先增加了33%,可达79 μmol/(h*m2)。样品的表征手段包括了分光光度计、X射线衍射仪及拉曼测试系统。通过实验发现,激光光束的扫描速率和线间距都会对催化性能产生影响,而其中的主要原因是激光诱导下异相结(非晶-金红石)的形成。异相结中费米能级的自准直对于氢气的产量起到了提高的作用。
Abstract: In thispaper, the photocatalytic activity enhancement of TiO2 thin filmswas realized by laser irradiation. The H2 yield of the as-irradiatedfilm is 79 μmol/(h*m2), which is 33% more than that of theas-deposited TiO2 film. Spectrophotometer, X-ray diffraction andRaman system were employed to characterize the samples. The results showed thatboth the scanning rate and line spacing of the laser modification have effectson photocatalytic activity. It suggests that a phase junction is formed betweenthe amorphous and rutile phases. The increment of H2 generation couldbe attributed to the alignment of Fermi levels in the phase junction.
关键数据
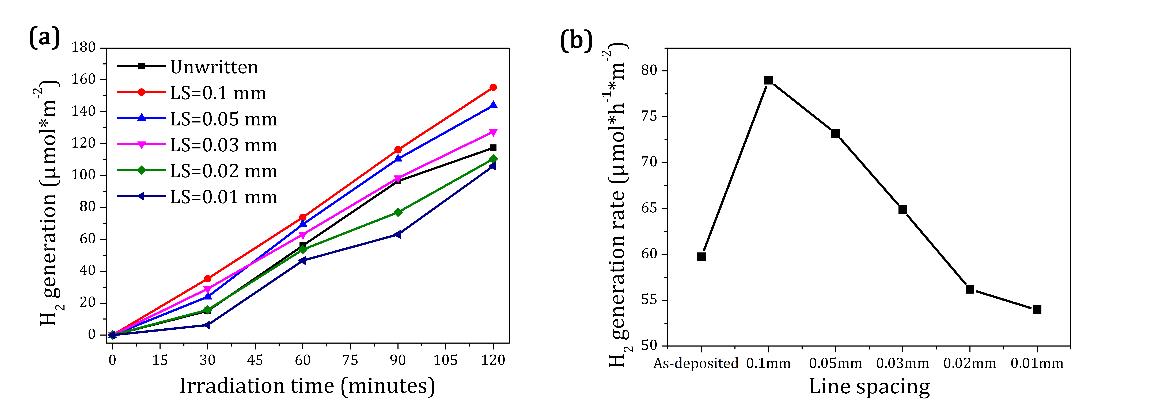
图1.(a)紫外光辐照下随线间距变化的不同时间下的氢气产量。
(b)每平方米样品每小时的氢气产量。
Figure1. (a) The H2 generation under UV-light irradiation as a function oftime with different line spacing (LS). (b) The calculated H2generation per hour per square meter.
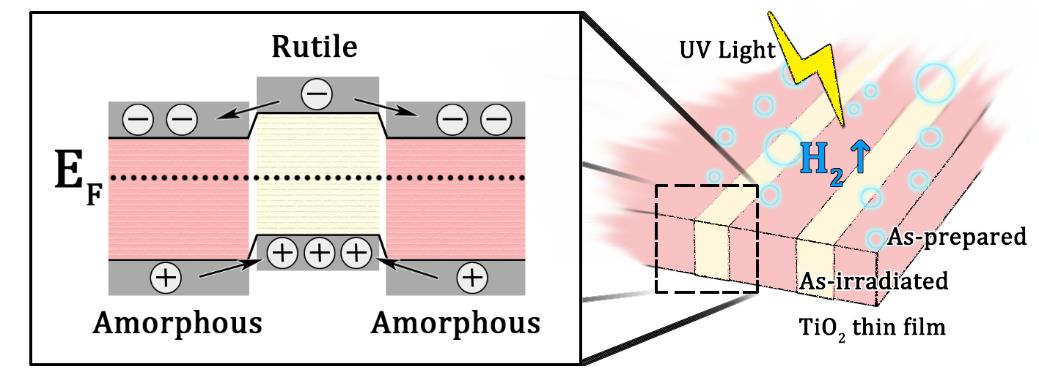
图2.二氧化钛薄膜中不同晶相之间的光生电子与空穴的迁移方式示意图。
Figure2. The schematic of photo-generated electrons and holes migration in phasejunction of the TiO2 thin film.
4.C. Fang,B.Dai, Q. Xu, R. Zhuo, Q. Wang, X. Wang, and D. Zhang, “Hydrodynamicallyreconfigurable optofluidicmicrolens with continuous shape tuning from biconvexto biconcave,”Optics Express, vol.25, no. 2, pp. 888–897, Jan. 2017.(IF=3.344)
基于流体动力操控的焦距连续可调的光流控微透镜
摘要:本文描述了一种平面内流体动力可重构的光流体透镜,两股低折射率溶液和两股高折射率溶液在两根微管道内形成层流,流入到扩展的腔体中,形成透镜。在这个扩展腔中,低折射率溶液作为包层,将高折射溶液流体夹在中心。流体间的界面可以通过实时控制两种流体的速度进行灵活的操纵。最终,形成了不同曲率的双凸和双凹透镜。通过调节透镜,能够连续操纵光束从准直到发散。
Abstract:This paper presents an in-planehydrodynamically reconfigurable optofluidicmicrolens, which is formed by thelaminar flow of two streams of a low-refractive-index fluid and two streams ofa high-refractive-index fluid in the two microchannels connecting to anexpansion chamber where the microlens finally forms. In the expansion chamber,the stream of high-refractive-index fluid, acting as core, is sandwiched by thetwo streams of lowrefractive-index fluid, acting as cladding. The interfacesbetween the streams can be flexibly manipulated by controlling the flow rateratio between the two fluids in real time. Thus, the biconvex and biconcavemicrolens with different curvatures can be formed. By adjusting the microlens,the light beam can be continuously manipulated from focusing to collimation andthen to divergence.
关键数据
本文提出了一种结构简单的基于流体动力学可重构的二维平面光流体透镜。四股流体形成的层流最终流入扩展腔体中形成透镜。两股低折射率溶液和两股高折射率溶液在两根微管道内形成层流,流入到扩展的腔体中,形成透镜。在这个扩展腔中,低折射率溶液作为包层,将高折射溶液流体夹在中心。中心层和包层之间的流体界面可通过控制两种流体的速度来灵活调节。中间层的流体可以形成不同曲率的双凸透镜和双凹透镜。通过调节透镜的形状,能够连续操纵导入芯片内的光束,使光束在聚焦、准直、发散三个状态连续可调。并且,在每个状态下,微透镜的焦距具有很大的调节范围。在研究中,通过理论建模,预测了微透镜的形状变化,并在实验中证实了微透镜变化的可行性,实现了光束的连续操纵。在实验中,微透镜的焦距可以从2.75mm(聚焦)经准直变化到-1.21mm(发散)。该可调透镜有望用于各种微流体器件及芯片实验室应用中。

透镜形成及操作原理
Theoperation principle of the proposed microlens.
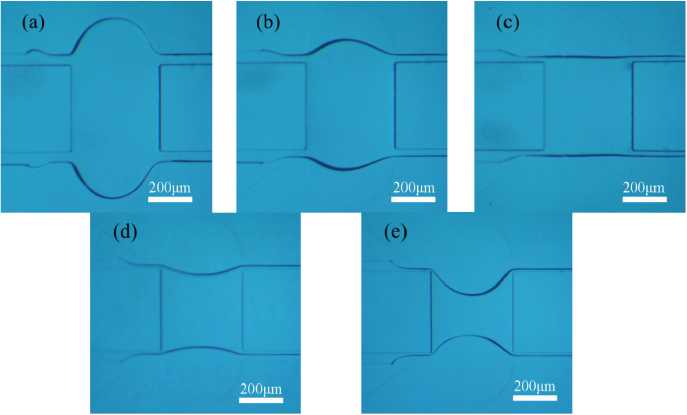
各种形状的透镜
Variationof microlenses
通过控制液体流速调节光束聚焦、准直及发散
Manipulatingthe focal distance of the microlens by adjusting the flow rate ratio betweencalcium chloride solution and silicone oil.
Anin-plane hydrodynamically reconfigurable optofluidicmicrolens with simplestructure is proposed. The mircolens can be produced at the two ends of theexpansion chamber by laminar flow of four streams of two fluids. The interfacesbetween the core streams and the cladding streams can be flexibly adjusted bycontrolling the flow rate ratio of the two fluids. The microlens can be shapedinto biconvex and biconcave. Thanks to the microlens shape tuning, the focustuning has a wide range, continuously from focusing to diverging viacollimation. Experiments are carried out to verify the concept. In theexperiment, a wide focus tuning range from 2.75 (focusing) to –1.21 mm(diverging) via collimation is achieved. The shape change of the microlens isvisualized and the light manipulation is demonstrated. The proposedtuneablemicrolensis a promising candidate for various microfluidic orlab-on-a-chip applications.
5.H. Lin, K. Imakita, M. Fujii, C. Sun, B. Chen, T. Kanno, and H. Sugimoto,“New insights intothe red luminescent bovine serum albumin conjugated gold nanospecies”, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, Vol. 691, pp 860-865, Jan. 2017. (IF=3.014)
对牛血清蛋白配位亚纳米尺度金红光发射的新认识
摘要:本论文工作成功合成了具有红光发射、含有不同Au0原子和Au+离子总数/每牛血清蛋白分子(AuTN/BSA)的牛血清蛋白配位亚纳米尺度金(BSA-Au)。实验结果表明相比AuTN/BSA,pH值对BSA-Au的发光性能具有更大影响。观察到了BSA-Au样品pH值敏感的可逆发光变化(红光发射的峰值波长移动:Δλ=40 nm)。这一实验现象同BSA-Au样品红光发射大的斯托克斯位移和单重态-三重态混合发光衰减等现象共同表明BSA-Au样品的发光特征与金属有机配合物的发光特征非常符合。
Abstract:Red luminescent bovine serum albumin conjugated goldnanospecies (BSA-Au) containing different total numbers of gold atoms and ionsper one BSA molecule (AuTN/BSA) were synthesized. It is shown that pH has moreinfluence on the emission properties than AuTN/BSA. pH sensitive and reversibleemission variation (shift of the red emission peak wavelength, Δλ=40 nm) wasobserved for the red emission from the BSA-Au samples. Together with the largeStokes shift in emission and the mixed singlet-triplet emission decay, it issuggested that the red emission from the BSA-Au samples agrees well with thefeatures of metal-organic complexes.
关键数据
以金、银为代表的亚纳米尺度贵金属颗粒由于其新奇的发光现象、较高的荧光量子产额、发光在一定条件下的开/关可控等特性使得其在生物荧光探针、化学传感器、光存储/光编码、无稀土荧光粉等领域显示出了很好的应用前景。然而,尽管亚纳米尺度贵金属颗粒在光学、光子学领域展现出诸多应用前景, 目前人们对其发光机理并不十分清楚,因此,十分有必要在充分探明亚纳米尺度金、银发光颗粒精细结构的基础上对其发光机理做进一步深入解析。
对此,本论文工作成功合成了具有红光发射、含有不同Au0原子和Au+离子总数/每牛血清蛋白分子(AuTN/BSA)的牛血清蛋白配位亚纳米尺度金(BSA-Au)。实验结果表明相比AuTN/BSA,pH值对BSA-Au的发光性能具有更大影响。观察到了BSA-Au样品pH值敏感的可逆发光变化(红光发射的峰值波长移动:Δλ=40 nm)。这一实验现象同BSA-Au样品红光发射大的斯托克斯位移和单重态-三重态混合发光衰减等现象共同表明BSA-Au样品的发光特征与金属有机配合物的发光特征非常符合。
Due tothe advantages such as low toxicity, high photo-bleaching resistance, andtunable emission energy, etc., organic molecules stabilized few-atom goldnanoclusters (Au NCs) have shown promising applications in photo-catalysis,light harvesting, bio-imaging, and chemical sensors, etc. Though variousapplications have been demonstrated, the exact luminescence mechanism of thefew-atom gold nanospecies is still not sufficiently clear.
Here inthis work we systematically investigated optical properties of the BSAconjugated Au nanospecies (short for BSA-Au) containing different total numbersof gold ions and atoms per one BSA molecule (AuTN/BSA), to help understand thestructure of the luminescent Au nanospecies conjugated by BSA. The motivationof this work is trying to disclose in terms of emission whether there is anyintrinsic difference between BSA-Au complexes and BSA stabilized Au NCs.It isshown that pH has more influence on the emission properties than AuTN/BSA. pHsensitive and reversible emission variation (shift of the red emission peakwavelength, Δλ=40 nm) was observed for the red emission from the BSA-Ausamples. Together with the large Stokes shift in emission and the mixed singlet-tripletemission decay, it is suggested that the red emission from the BSA-Au samplesagrees well with the features of metal-organic complexes.
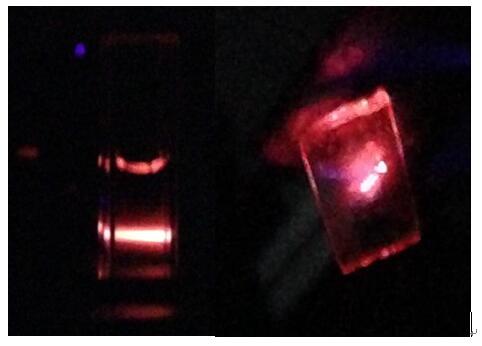
Pictures of the red luminescent BSA-Au nanospecies under the 405 nmexcitation: (left)solution, (right) solid film formed from solution viaevaporation at room temperature.
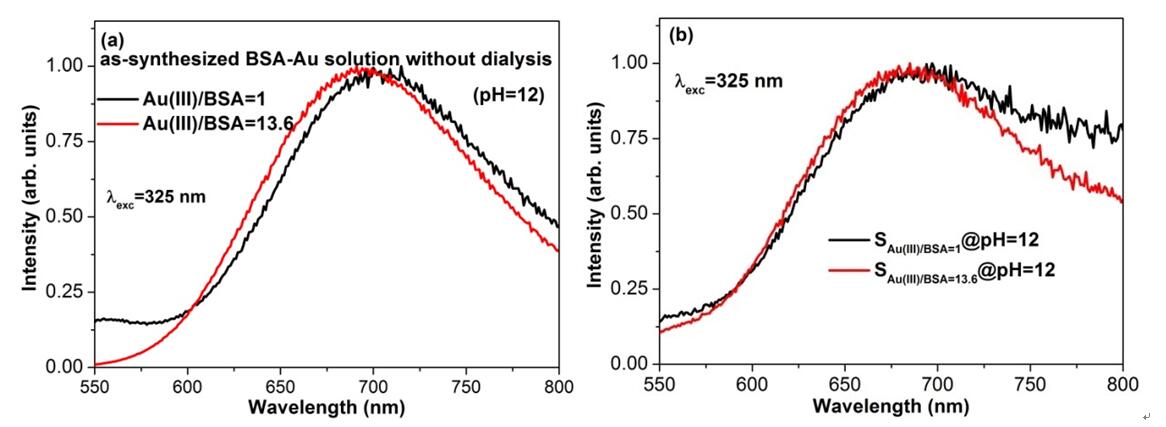
PL spectra for the two as-synthesized BSA-Au solutions (Au(III)/BSAratios=1 and 13.6, respectively) without dialysis (a); and PL spectra of SAu(III)/BSA=1and SAu(III)/BSA=13.6 at pH=12 (b).
6.WenzuoWei, Ruijin Hong, Jinxia Wang, Chunxian Tao and Dawei Zhang, Electron-beamirradiation induced optical transmittance enhancement for Au/ITO and ITO/Au/ITOmultilayer thin films, 33 (10), Journal of Materials Science& Technology, 2017 (1107-1112)(IF=2.267)
电子束辐照诱导的具有透射增强特性的Au/ITO和ITO/Au/ITO复合薄膜
摘要:本文研究了电子束辐照诱导对Au/ITO和ITO/Au/ITO复合薄膜光电性能的影响,并用X射线衍射仪、原子力显微镜、四探针探测仪和紫外—可见—近红外双光束分光光度计分别检测样品经电子束辐照诱导前后的光电特性变化情况。结果表明,电子束辐照诱导能够增强样品的结晶度、降低其方块电阻以及提高其在不同波段的透过率。
Abstract:Electron beam (EB) irradiation experiments on Au/ITO and ITO/Au/ITO multilayerthin films are reported. The structure and the optical-electrical properties ofthe samples were investigated by X-ray diffraction, atomic force microscopy,four-point probe resistivity measurement system, and UV–vis-NIR double beamspectrometer, respectively. Those results show that the EB irradiation has theeffects of improving the crystalline of samples, widening the optical band gapof both thin films, reducing the sheet resistance, and improving thetransmittance of samples.
关键数据
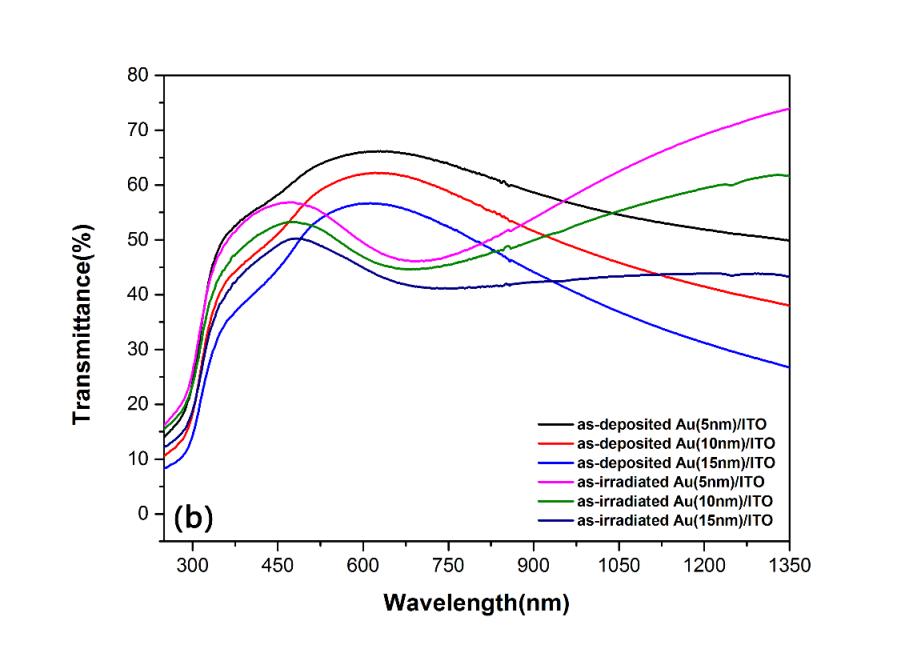
图1电子束诱导下Au/ITO双层薄膜的近红外透过率提高
Fig.1 The NIRtransmittance of Au/ITO bilayer is enhanced after EB irradiation
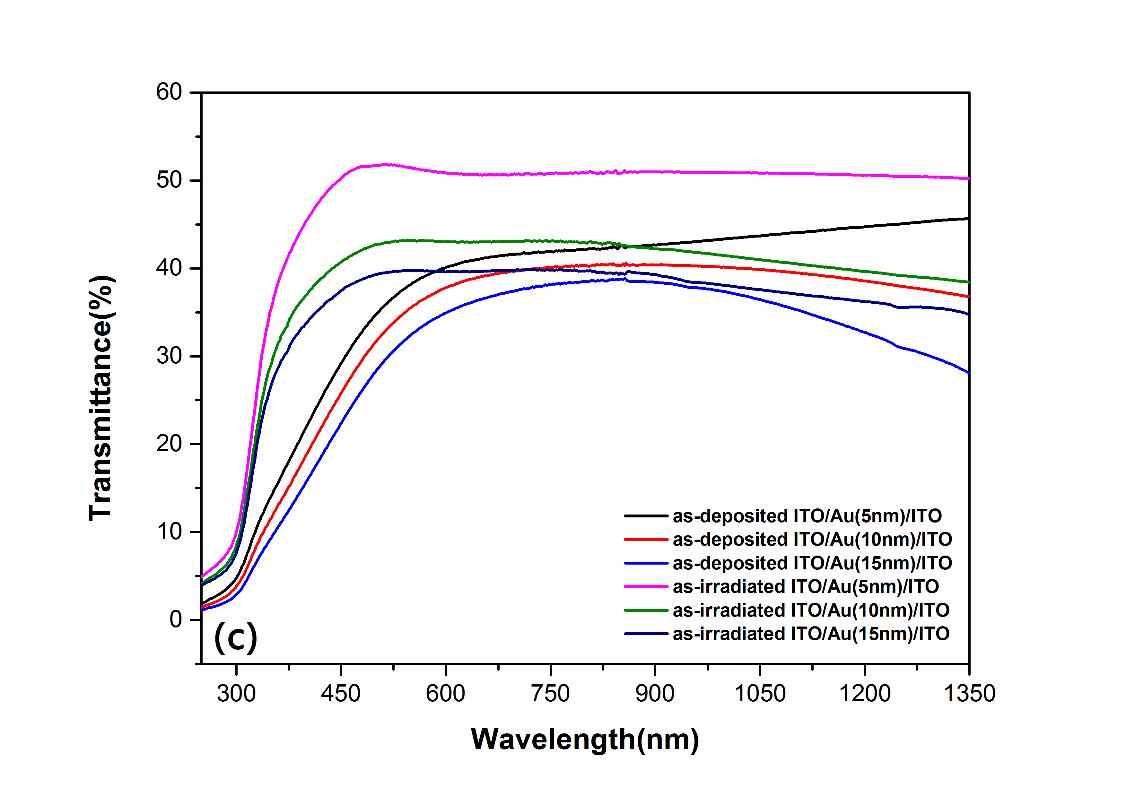
图2电子束诱导下ITO/Au/ITO双层薄膜的可见光透过率提高
Fig. 2 Thevisible transmittance of ITO/Au/ITO bilayer is enhanced after EB irradiation
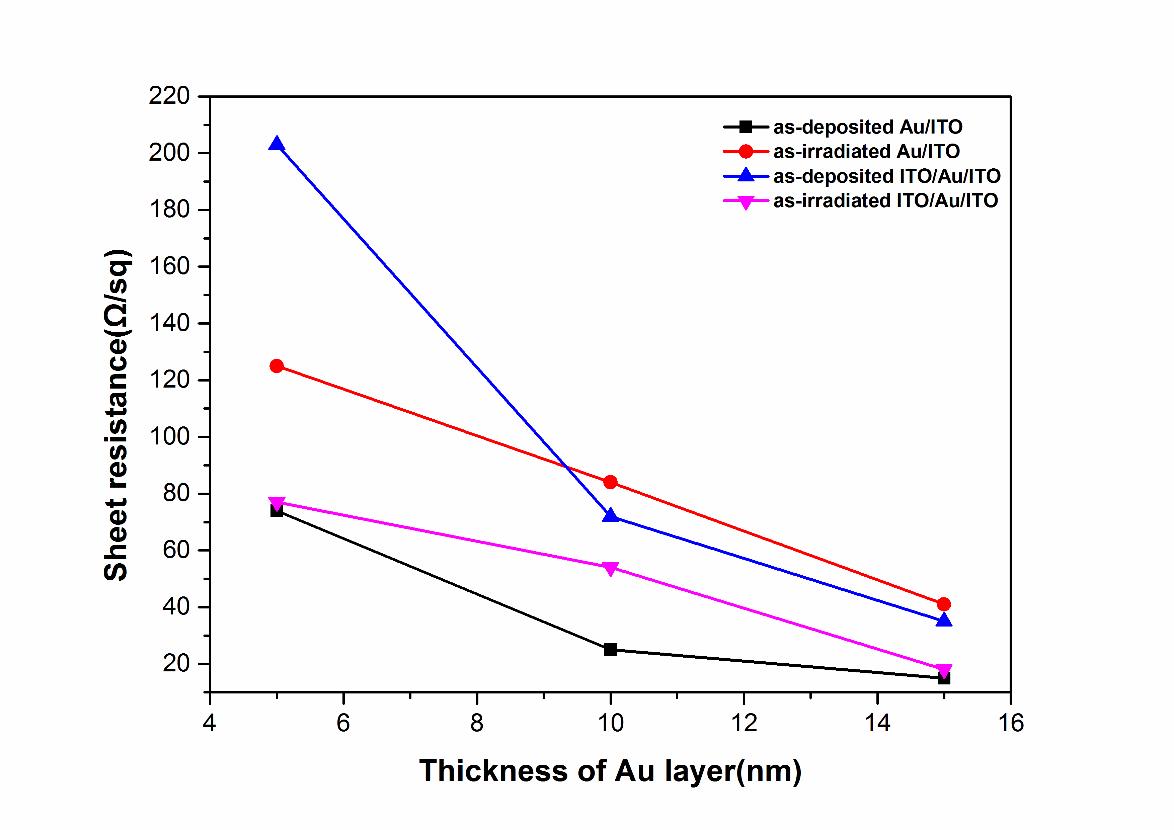
图3电子束诱导下ITO/Au/ITO双层薄膜的方块电阻下降
Fig. 3 Thesheet resistance of ITO/Au/ITO trilayer is decreased after EB irradiation
7.B. Dai, S. Yin, Z. Gao, K. Wang, D. Zhang, S. Zhuang, and X. Wang, “Datacompression for time-stretch imaging based on differential detection andrun-length encoding,” J. Lightw. Technol., vol. 35, no. 23, pp. 5098–5104, Nov.2017 (IF=2.567)
基于差分检测及游程编码的高速成像数据压缩技术
摘要:本文提出了一种基于差分检测和游程编码的高保真数据压缩方法实现时域编码成像,系统中将空间图像信息映射到时域,然后由平衡光电探测器读出并实现图像重构。差分检测能够区分连续扫描的差异并消除相同的信号,检测之后,运行游程编码将连续的相同数据合并到单个数据中。数据解压后,可重建高保真度的图像。
Abstract:A high-fidelity data compression methodbased ondifferential detection andrun-length encoding is proposed foratime-stretch imaging system, where a spatial image is mapped tothe time domainand then read out by a balanced photodetectorfor image reconstruction.Differential detection is capable of distinguishingdiscrepancy of consecutivescans and eliminating identicalsignals. After the detection, run-lengthencoding merges consecutiveidentical data to a single data. After the datadecompression, the image of high fidelity can be reconstructed.
关键数据
本文提出了基于差分检测和游程编码的时域编码成像系统实现数据压缩。差分检测消除了连续扫描的相同信号并输出之间的差异扫描。在差分检测之后,数据流中相同数据的可能性增加,这有利于通过使用游程编码来进行数据压缩。设计并搭建了77.76MHz线扫描成像系统,实验证明了该方案的可行性。由于游程编码是无损的,保证了重建图像的保真度。所提出的方案可以有效地减少数据量计算复杂度低。在快速在线数据压缩应用上前景广阔,适用于时域编码高速成像系统。
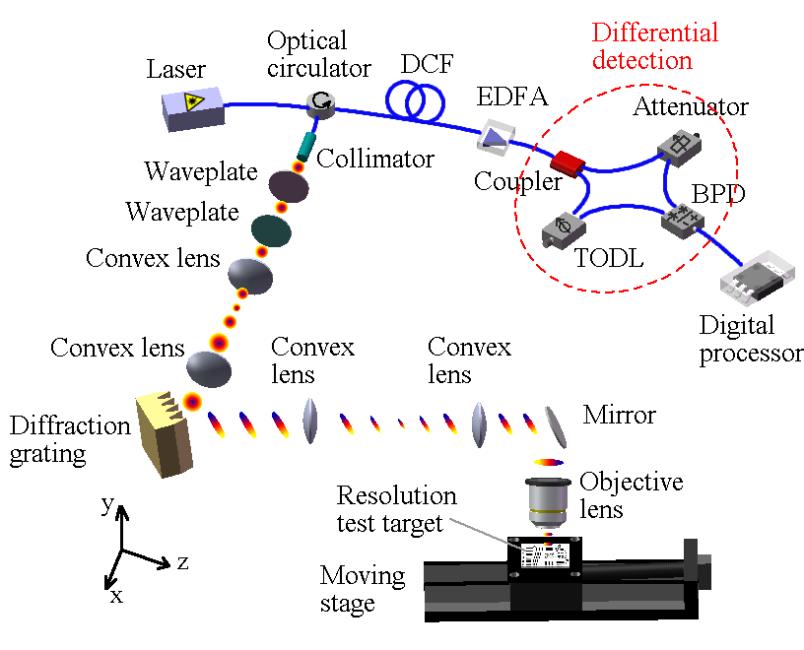
成像系统方案
Schematicof the proposed imaging system
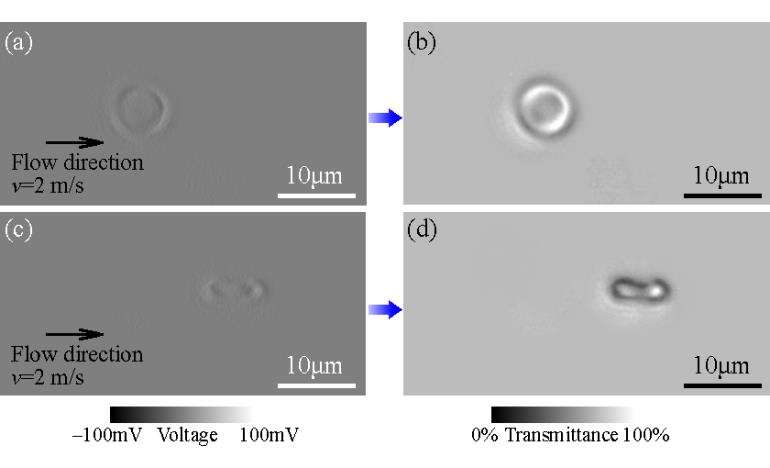
利用差分检测方法对单个红细胞进行高速成像
The images of red blood cells obtainedby the differential detection.
Thetime-stretch imaging system with differentialdetection and run-length encodingis proposed for datacompression. The differential detection eliminatesidentical signalsof consecutive scans and outputs the discrepancy between thescans. After differential detection, the possibility of identicaldata in thedata stream is increased, which benefits to datacompression by using run-lengthencoding. The 77.76MHz line scanimaging system is experimentally demonstrated.Since run-length encodingis lossless, the fidelity of the reconstructed imageis guaranteed.The proposed scheme can efficiently reduce the data volume andhas low computation complexity. It is a promising fast onlinedata compressionmethod for time-stretch imaging system.
二、课题组年度发表SCI论文(24篇)
| 论文标题 | 期刊 | 第一/通讯作者 | 分区 |
1 | New insights into the red luminescent bovine serum albumin conjugated gold nanospecies | Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017年1月 | 林辉 | 1 |
2 | Miniaturized Gel Electrophoresis System for Fast Separation of Nucleic Acids | Sensors & Actuators B - Chemical, 2017年07月 | 李振庆 | 1 |
3 | Fabrication of microlens array by thermally harnessing surface tension of photosensitive gel film beneath microholes | ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017年4月 | 张大伟/戴博 | 2 |
4 | Hydrodynamically reconfigurable optofluidic microlens with continuous shape tuning from biconvex to biconcave | Optics Express, 2017年1月 | 方朝龙/张大伟 | 2 |
5 | Laser Induced Photocatalytic Activity Enhancement of TiO2 Thin Films | Optics Express, 2017年1月 | 荆铭/张大伟 | 2 |
6 | Date compression for time-stretch imaging based on differential detection and run-length encoding | Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2017年11月 | 戴博 | 2 |
7 | Electron-beam irradiation induced optical transmittance enhancement for Au/ITO and ITO/Au/ITO multilayer thin films | Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2017年10月 | 魏文左/洪瑞金 | 2 |
8 | Needle-Like Co-Mo-O with Multi-Modal Porosity for Pseudocapacitors | Materials Chemistry And Physics, 198 (2017), 258-65. | 张大伟 | 3 |
9 | Ultra-Broadband Excitations of PlasmonicWaveguides by Bowtie Apertures | Plasmonics, 12, 4, 1257-1262(AUG 2017) | 文静/张大伟 | 3 |
10 | Plasmonic holographic metasurface for generation of vector optical beams | Photonics Journal,2017-01-11 | 文静/张大伟 | 3 |
11 | Optofluidic tunable linear narrow-band filter based on Bragg nanocavity | IEEEPhotonics Journal, 2017年4月 | 方朝龙/张大伟 | 3 |
12 | Electron-beam irradiation induced phase transformation, optical absorption and surface-enhanced Raman scattering of Indium tin alloy thin films | Superlattices and Microstructures, 2017-04 | 魏文左/张大伟 | 3 |
13 | Difference of SERS ability from titanium oxide films by Ti3+ self-doping | Optical Materials, 2017-11 | 荆铭/洪瑞金 | 3 |
14 | Real-time Tracking DNA Fragments Separation by Smartphone | Journal of Visualized Experiments, 2017-06 | 李振庆 | 3 |
15 | Tailorable Elastomeric Grating With Tunable Groove Density Gradient | IEEE Photonics Journal, 2017年10月 | 盛斌 | 3 |
16 | Characteristics of Guided-Mode Resonance Filter With Elliptically Polarized Incident Light | IEEE Photonics Journal, 2017-02 | 王琦 | 3 |
17 | Measuring grating periods by diffraction method with a fore-end light path comprising fused fiber couplers and fiber port collimators | Review of Scientific Instruments 88, 106102 (2017.10) | 盛斌 | 3 |
18 | Quantum dot based detections of propagating plasmonic modes excited by bowtie antennas | Laser Physics, 2017-01-13 | 文静/张大伟 | 4 |
19 | Arbitrary continuous nano-marks generated by multifocal spot arrays for controllable laser printing | Laser Physics, 2017-02-17 | 文静/张大伟 | 4 |
20 | Research on straightness error compensation of grating ruling machine | Spectroscopy and spectral analysis, 2017.3 | 黄元申 | 4 |
21 | Thickness Dependence of Ultraviolet-Excited Photoluminescence Efficiency of Lumogen Film Coated on Charge-Coupled Device | Current Optics and Photonics, 2017年8月 | 陶春先 | 4 |
22 | Broadband polarizing beam splitter based on two-layer metal grating with a high refractive index dielectric layer | Optik, 2017-07 | 王琦 | 4 |
23 | Optical properties study of silicone polymer PDMS substrate surfaces modified by plasma treatment | Materials Research Express, 2017年10月 | Ali Zahid/张大伟 | 4 |
24 | Portable organic gas detection sensor based on the effect of guided moderesonance | AIP Advances 7, 015031 (2017); | 郭亮/王琦 | 4 |
三、年度在研科研项目(2017年新增15项)
| 项目名称编号 | 项目级别 | 负责人 | 获批时间 |
1 | 表面等离激元干涉快速调控结构光照明超分辨成像的研究 | 国家自然科学面上基金项目 | 张大伟 | 2017 |
2 | 基于透明导电氧化物光谱调控与剪裁薄膜性能研究 | 国家自然科学面上基金项目 | 洪瑞金 | 2017 |
3 | 用于在体捕获红细胞的表面等离子体超透镜光镊系统的研究 | 国家自然科学青年基金项目 | 文静 | 2017 |
4 | 超精密光学制造军民融合公共服务平台 | 省部级 | 张大伟 | 2017 |
5 | 高性能、便携式荧光检测系统工程化研制 | 省部级 | 洪瑞金 | 2017 |
6 | 近红外/中波红外高透过率、低强度调制、耐高能激光透明导电膜 | 省部级 | 洪瑞金 | 2017 |
7 | 双光束超分辨率光驱样机小型化技术研究 | 省部级 | 文静 | 2017 |
8 | 面向智能仪器设计的嵌入式系统课程培训 | 教育部 | 杨海马 | 2017 |
9 | 空间量子光通信中偏振信标姿态检测及符号式跟踪方法研究 | 省部级 | 杨海马 | 2017 |
10 | 高精密光谱仪应用功能拓展及测试方法共享研究 | 省部级 | 韩朝霞 | 2017 |
11 | 953光学器件的技术开发 | 军工类 | 洪瑞金 | 2017 |
12 | 光学镜片放射性辐照试验 | 军工类 | 洪瑞金 | 2017 |
13 | 激光/光学晶体加工表面损伤机理及其修复、优化工艺技术研究 | 科技部 | 陶春先 | 2017 |
14 | 耳道三维轮廓测量系统 | 苏州立人听力设备有限公司 | 杨海马 | 2017 |
15 | 宽光谱大口径阶梯灰度感光测试系统研制 | 企业委托 | 黄元申 | 2017 |
16 | 猪病高通量检测技术及设备研究 | 国家重点研发计划重点专项 | 张大伟 | 2016 |
17 | 基于一次性密码多符号重叠编解码的保密光通信技术的研究 | 国家自然科学基金项目 | 戴博 | 2016 |
18 | 基于光流控芯片技术的新型涡旋光束产生方法 | 省部级 (上海市青年科技英才扬帆计划) | 王凯民 | 2016 |
四、国内发明专利授权(12项)
| 专利名称 | 专利级别 | 发明人 | 授权日期 |
1 | 一种线性渐变滤光片中间楔形谐振腔层的制备方法 | 发明专利 | 盛斌,陈鹏,黄元申,张大伟 | 2017.5.31 |
2 | 能够增强电荷耦合元件紫外响应能力的光学薄膜及制备 | 发明专利 | 陶春先,崔潇,何梁,洪瑞金,张大伟 | 2017.1.18 |
3 | 检测导模共振滤波器光谱的系统及方法 | 发明专利 | 王琦,王建宇,张大伟,李业,黄元申,盛斌,倪争技 | 2017-7-14 |
4 | 基于帧间差分背景图像的视频图像压缩感知重构方法 | 发明专利 | 张雷洪 | 2017.6 |
5 | 检测凹面光栅分辨率和衍射效率的装置及方法 | 发明专利 | 苏仰庆,黄元申,杨海马,王光斌,黄运柏 | 2017-01-11 |
6 | 一种打工业蜡大米的无损鉴别方法 | 发明专利 | 李柏承,赵曼彤,周瑶,侯宝路,徐邦联,张大伟,王琦,黄元申 | 2017-05-03 |
7 | 一种光学希尔伯特变换与微分运算系统 | 发明专利 | 戴博,卓然,汪东,张大伟,黄元申,王琦,孔小芳 | 2017-05-31 |
8 | 基于移动通信全球系统的窗户自动控制装置 | 发明专利 | 文静,王康,钟阳万,曾媛,张大伟 | 2017-11-28 |
9 | 钢球表面检测装置 | 发明专利 | 杨海马、王光斌,马贤淑,黄凯,毕继耀,刘瑾,宋佳,陈鑫元 | 2017-11-10 |
10 | 一种测温元件扫描网络结构以及温度场测量装置 | 发明专利 | 陈成、杨海马、涂建坤、李筠、刘瑾、黄元申、方睿、陈鑫元、姚隆龙、王祖德、严谨 | 2017-04-26 |
11 | 一种基于关联成像的距离测量方法 | 发明专利 | 秦川,魏凯,戴博,张大伟,王琦,陶春先 | 2017-07-18 |
12 | 医用静脉输液监测系统 | 实用新型 | 王进霞,洪瑞金,陶春先,张大伟 | 2017-09-12 |
有关微纳光学器件与微纳光学材料方面的课题合作,请联系张大伟教授。
Emai:dwzhang@usst.edu.cn ; 微信号: 13764694608;